Understanding Genophobia: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
Are you or someone you know struggling with an intense fear of sex or sexual intimacy? Genophobia is a complex and often misunderstood condition that can significantly disrupt your romantic life. This comprehensive guide explains what genophobia is, its causes, symptoms, and the most effective treatment options. If you’re seeking clarity and hope, keep reading to learn how therapy and understanding can help you reclaim a healthy, fulfilling intimate life.
What Is Genophobia? An Overview of the Fear of Sex
Genophobia, also known as the fear of sex or sexual intimacy, is a specific phobia classified under DSM criteria. It involves an overwhelming and persistent fear that impairs daily functioning and relationships. People with genophobia often experience intense anxiety just contemplating or approaching sexual activity, which can lead to avoidance behaviors and emotional distress.
Recognizing the Symptoms and Signs of Genophobia
Physical Symptoms
Individuals with genophobia often experience physical reactions such as:
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Sweating
- Breadthlessness
- Headaches
- Muscle tension
- Fatigue
- Sleep disturbances
Behavioral and Emotional Signs
Behaviorally, those affected may:
- Make excuses to avoid intimacy
- Scream or withdraw during sexual encounters
- Sabotage relationships intentionally
- Shun dating altogether
- Alter their appearance to seem less desirable
Emotionally, sufferers often report feelings of embarrassment, shame, low self-esteem, trust issues, anger, and depression.
What Causes Genophobia? Deep Dive into Root Factors
The causes of genophobia are multifaceted and often involve a combination of factors:
- Trauma and Abuse: Sexual abuse, assault, witnessing violence, or experiencing rape trauma can link sex to danger, triggering phobia responses. According to 2016 research, trauma plays a significant role in developing genophobia.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like vaginismus, endometriosis, vulvodynia, erectile dysfunction, or premature ejaculation can amplify fears associated with pain or failure.
- Body Image and Performance Anxiety: Concerns about physical appearance or sexual performance can contribute to anxiety and fear.
- Cultural and Religious Taboos: Cultural beliefs or spiritual practices may associate sex with sin or shame, intensifying fear.
- Exposure to Explicit Media in Childhood: Early exposure to sexual content can distort perceptions and increase anxiety later in life.
- Genetics and Brain Wiring: Some individuals may have a predisposition due to genetics or neural wiring that enhances anxiety responses.
No single cause explains genophobia, but understanding these factors helps tailor effective interventions.
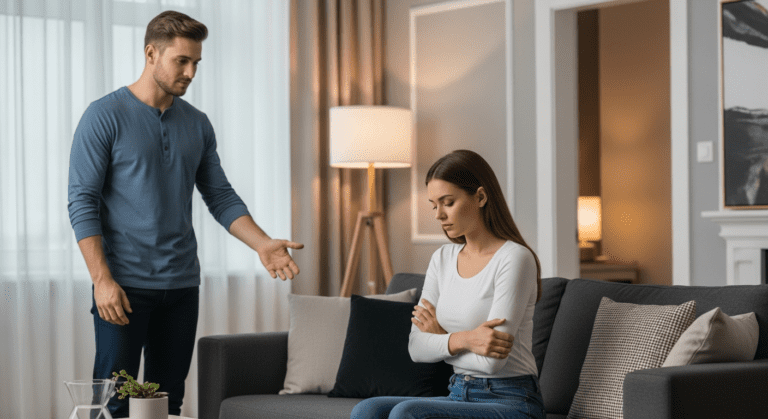
Impact of Genophobia on Relationships and Emotional Well-being
Living with genophobia can lead to significant emotional and relational challenges:
- Feelings of isolation and loneliness
- Decreased self-esteem and self-worth
- Trust issues and emotional distance
- Anger, frustration, and resentment
- Depression and anxiety disorders
For those craving intimacy without shame, breaking free from this fear can be transformative. Recognizing the emotional toll emphasizes the importance of seeking help.
Treatment Options for Genophobia: Path to Healing
Psychotherapy Approaches
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps reframe negative thoughts about sex and develop healthier beliefs.
- Exposure Therapy: Gradual desensitization to feared stimuli, starting from simple elements and progressing to full intimacy.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): Specifically targets trauma memories linked to sexual fears.
- Sex Therapy: Addressing performance anxiety, communication skills, and body positivity through mindfulness and behavioral techniques.
Medication Support
In some cases, medications such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs may be prescribed to manage overwhelming anxiety symptoms, enabling clients to engage more effectively in therapy.
Additional Strategies and Resources
- Addressing underlying pain issues like vaginismus or vulvodynia before tackling fear of sex
- Educational resources and support groups for a sense of community and shared experience
- Online therapy platforms offering flexible, confidential treatment options (see more)
Proactive approaches combining therapy, medical management, and self-awareness are the most successful path forward.
Frequently Asked Questions About Genophobia
1. Can genophobia be cured?
While there is no universal cure, many individuals experience significant improvement with professional therapy and support. Treatment outcomes depend on underlying causes and commitment to therapy.
2. How long does treatment for genophobia typically take?
The duration varies, but many see progress within several months of consistent therapy. Some may require longer-term intervention, especially if trauma is involved.
3. Is genophobia common?
It’s more common than often acknowledged, affecting a subset of individuals who experience severe anxiety related to sexual activity. Open discussion and medical help can facilitate recovery.
4. Are medications effective for genophobia?
Medications can help manage anxiety symptoms to facilitate therapy but should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan under medical supervision.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Your Sexual Life
Living with genophobia can feel isolating and overwhelming, but recovery is possible. Understanding the root causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking professional help are crucial steps towards overcoming the fear of sex. With the right combination of therapy, medical support, and self-awareness, you can rebuild trust, confidence, and intimacy in your life.
Remember, you’re not alone, and help is available. If you want to explore more about building healthy relationships or managing intimacy issues, check out resources like this guide for practical advice.




0 Comments